Rotary Kiln




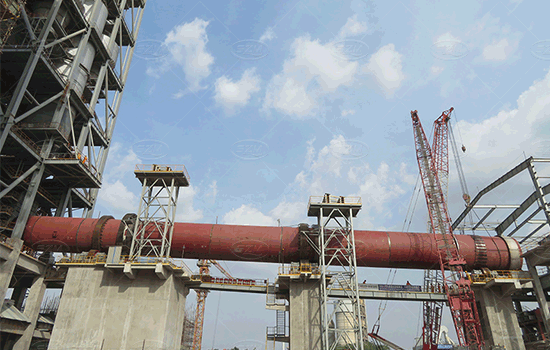

Rotary Kiln
Rotation Speed:0.1–5(r/min)
Capacity:180-10000(t/d)
Specification:Φ2.5×40-Φ6.0×95
Applied Materials:Roasting cement clinker in the industries of metallurgy, refractory matter and chemical plant
Features and technology advantages of Rotary Kiln
The rotary kiln refers to the rotary calcination kiln (commonly known as rotary kiln), which is similar in shape to the rotary kiln, also known as the rotary kiln, and belongs to the category of building materials and equipment. Rotary kiln can be divided into cement kiln, metallurgical and chemical kiln and lime kiln according to different materials. Cement kilns are mainly used to calcine cement clinker, which are divided into dry production cement kilns and wet production cement kilns. Metallurgical and chemical kilns are mainly used for magnetization roasting of lean iron ore in iron and steel plants of metallurgical industry; Oxidation roasting of chromite and nickel iron ore; Refractory plant roasting high-alumina bauxite ore and aluminum plant roasting clinker and aluminum hydroxide; Chemical plants roast chromium ore sand, chromium ore powder and other minerals. Lime kiln (i.e. active lime kiln) is used to roast active lime and light-burned dolomite used in iron and steel plants and ferroalloy plants.
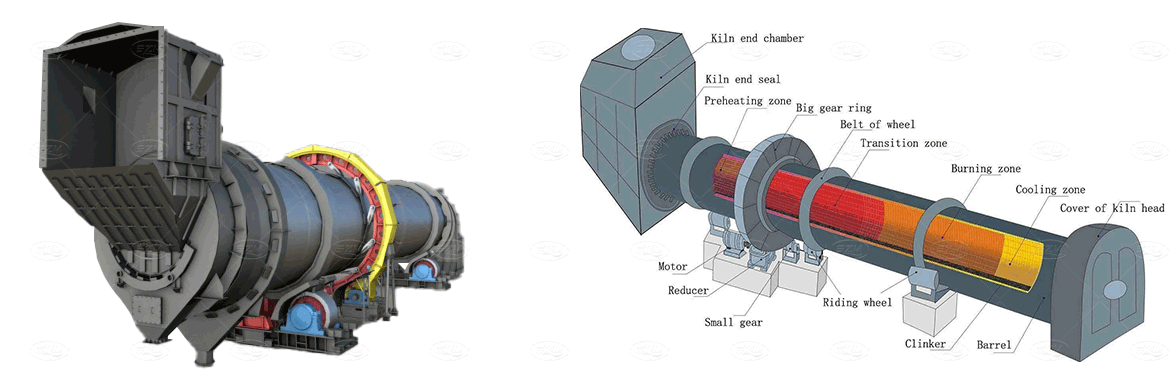
1. Building materials industry: slag drying and the calcination of cement, clay, limestone, refractory material, etc;
2. Metallurgical industry: sintering ore, concentrate, intermediate; the smelting of iron, aluminum, copper, zinc, tin, nickel, tungsten, chromium, file and other non-ferrous and ferrous metals;
3. Environmental protection industry: use the waste as fuel; use the cement kiln to burn hazardous waste, waste to achieve quantitative reduction, harmless and resourceful of waste;
4. Chemical Industry: magnetization roasting of iron ore to enhance its magnetism; it uses rotary kiln for the production of soda, calcined phosphate fertilizer, barium sulfide, etc.
Advantages of Rotary Kiln
1. The vertical preheater with good structure and low pressure loss can effectively improve the preheating effect. The decomposition rate of preheated limestone into the kiln can reach 20 to 25%, and 10-15mm fine limestone can be directly used.
2. Reliable combined scale seal at both ends of rotary kiln. Make the air leakage coefficient less than 10% and use composite refractory materials to reduce the radiation heat loss.
3. The filled and ventilated circular or square vertical cooler can make the lime temperature of the cooler reach 800 ℃ ambient temperature, which is convenient for transportation and storage, and can preheat the secondary air into the kiln to above 700 ℃, reducing the moving parts and special materials.
Working principle of Rotary Kiln
Raw meal powder is fed into the kiln shell from the lower end of the kiln tail shell. Due to the inclination and slow rotation of the kiln shell, the material has a compound movement that is rolling in the circumferential direction and moving from the high temperature to the low end in the axial direction. Raw meal is decomposed and burned in the kiln, and then discharged from the bottom end of the kiln shell after burning cement clinker, and then enters the cooler. The fuel is injected from the kiln head and burned in the kiln. The heat generated heats the raw meal to make it calcined into clinker. The hot air formed in the process of material exchange enters the kiln system through the kiln feed end, and finally is discharged into the atmosphere through the chimney.
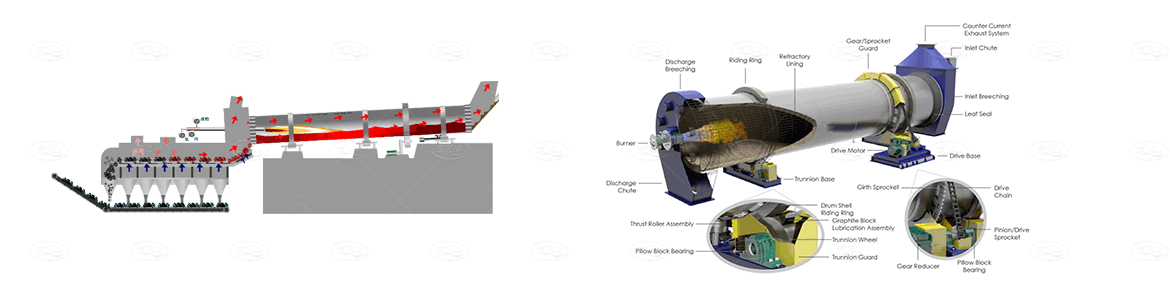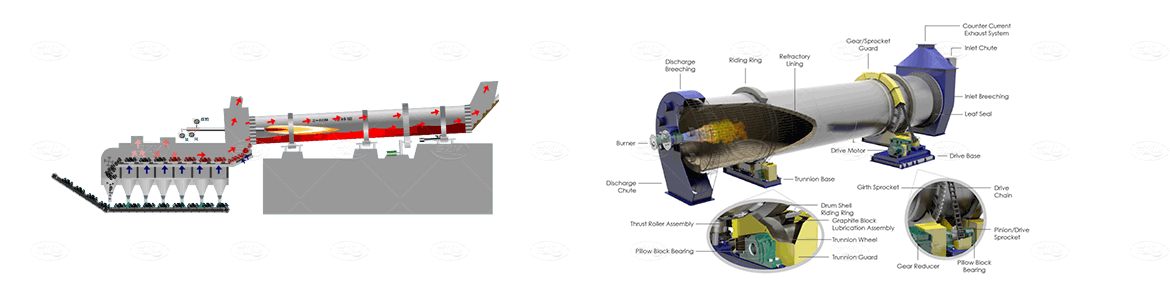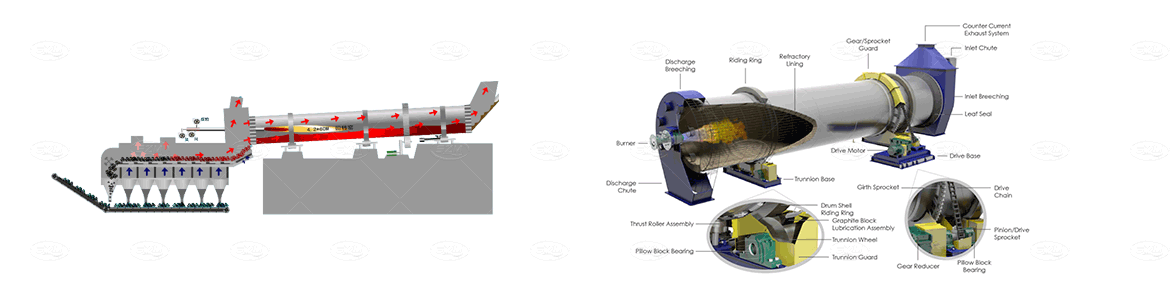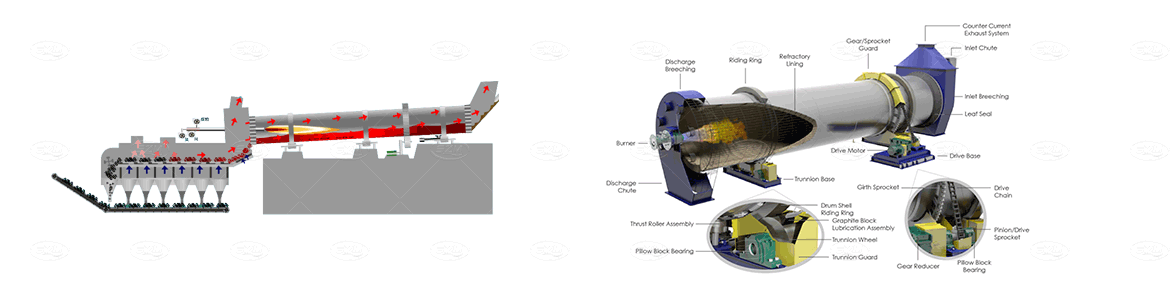
Product Data
Technical Data of Rotary Kiln:
| Product specification | Kiln body size | Motor power | Total weight | Remarks | ||||
| (m) | Diameter(m) | Length(m) | Slope(%) | Capacity(t/d) | Speed(r/min) | (kw) | (t) | |
| Φ2.5×40 | 2.5 | 40 | 3.5 | 180 | 0.44-2.44 | 55 | 149.61 | |
| Φ2.5×50 | 2.5 | 50 | 3 | 200 | 0.62-1.86 | 55 | 187.37 | |
| Φ2.5×54 | 2.5 | 54 | 3.5 | 280 | 0.48-1.45 | 55 | 196.29 | Decomposing kiln outside the kiln |
| Φ2.7×42 | 2.7 | 42 | 3.5 | 320 | 0.10-1.52 | 55 | 198.5 | ---- |
| Φ2.8×44 | 2.8 | 44 | 3.5 | 450 | 0.437-2.18 | 55 | 201.58 | Decomposing kiln outside the kiln |
| Φ3.0×45 | 3 | 45 | 3.5 | 500 | 0.5-2.47 | 75 | 201.94 | ---- |
| Φ3.0×48 | 3 | 48 | 3.5 | 700 | 0.6-3.48 | 100 | 237 | Decomposing kiln outside the kiln |
| Φ3.0×60 | 3 | 60 | 4 | 800 | 0.3-2 | 100 | 310 | ---- |
| Φ3.2×50 | 3.5 | 50 | 4 | 1000 | 0.6-3 | 125 | 278 | Decomposing kiln outside the kiln |
| Φ3.3×52 | 3.3 | 52 | 3.5 | 1300 | 0.266-2.66 | 125 | 283 | Preheating decomposition kiln |
| Φ3.5×54 | 3.5 | 54 | 3.5 | 1500 | 0.55-3.4 | 220 | 363 | |
| Φ3.6×70 | 3.6 | 70 | 3.5 | 1800 | 0.25-1.25 | 125 | 419 | |
| Φ4.0×56 | 4 | 56 | 4 | 2300 | 0.41-4.07 | 315 | 456 | |
| Φ4.0×60 | 4 | 60 | 3.5 | 2500 | 0.396-3.96 | 315 | 510 | |
| Φ4.2×60 | 4.2 | 60 | 4 | 2750 | 0.41-4.07 | 375 | 633 | |
| Φ4.3×60 | 4.3 | 60 | 3.5 | 3200 | 0.396-3.96 | 375 | 583 | |
| Φ4.5×66 | 4.5 | 66 | 3.5 | 4000 | 0.41-4.1 | 560 | 710.4 | |
| Φ4.7×74 | 4.7 | 74 | 4 | 4500 | 0.35-4 | 630 | 849 | |
| Φ4.8×74 | 4.8 | 74 | 4 | 5000 | 0.396-3.96 | 630 | 899 | |
| Φ5.0×74 | 5 | 74 | 4 | 6000 | 0.35-4 | 710 | 944 | |
| Φ5.6×87 | 5.6 | 87 | 4 | 8000 | Max4.23 | 800 | 1265 | |
| Φ6.0×95 | 6 | 95 | 4 | 10000 | Max5 | 950×2 | 1659 | |

